
This interactive map of the Basin and Range Province reveals earthquakes, faults, hazards, volcanoes, mines, and National Parks.
The links above to other interactives, video and animations offer detail about other basin-range features.
VIEW the interactive in a separate tab, by clicking on "Open Resource" then scroll over named features. (Note some browsers lack the plugins for rollovers.)
IRIS may be discontinuing these interactive animations in the future. This file is an HTML5 file that uses a browser to view.
Rolling over green buttons reveals:
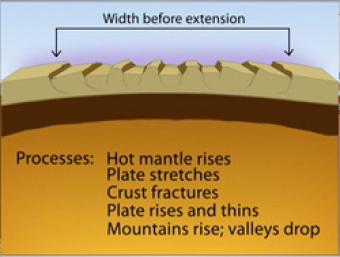
Over most of the last 30 million years, movement of hot mantle beneath the region caused the surface to dome up and then partially collapse under its own weight, as it pulled apart. Currently, there is very little actual stretching going on, and the small amount is concentrated on the Western and Eastern edges of the Basin and Range.
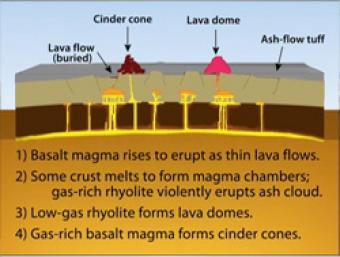
During Basin & Range extension, the plates pull apart, the mantle rises and melts due to lower pressures near the surface. The style of eruption depends on how long the magma sits in the crust and undergoes processes such as crystallization and melting and assimilation of wall rock.
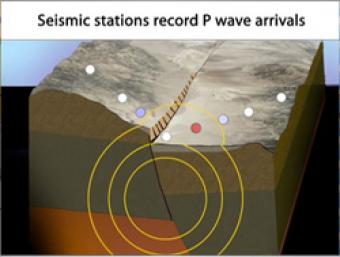
Cross section of the shallow crust in the Basin & Range. Earthquake produces seismic waves that bump an array of seismic stations. One station records the arrival of the seismic waves on a seismogram.
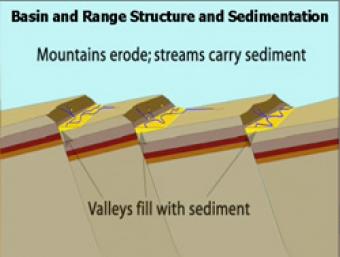
As extension and uplift occur, erosion and sedimentation happen simultaneously but at slower rates. As extension slows down, erosion and sedimentation can overcome mountain building.
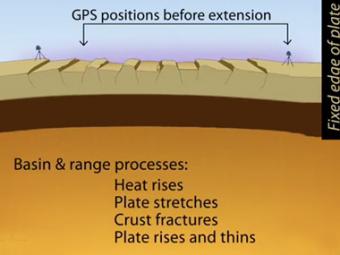
Simplified extension of the basin and range province as reflected in the GPS (global positioning system) stations at distant ends of the region. Tension created by movements of Earth's tectonic plates have stretched the earth's surface to the breaking point. The entire region has been pulled apart, fracturing the tectonic plates and creating large faults.

How can I demonstrate plate tectonic principles in the classroom?
Video lecture demonstrates the use of foam faults to demonstrate faults, and a deck of cards to demonstrate folds and fabrics in rock layers. Different types of faults include: normal (extensional) faults; reverse or thrust (compressional) faults; and strike-slip (shearing) faults.
We encourage the reuse and dissemination of the material on this site as long as attribution is retained. To this end the material on this site, unless otherwise noted, is offered under Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license