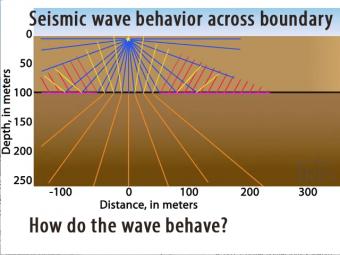
What happens when seismic waves hit a boundary between faster and slower layers?
This introduction to seismic wave behavior describes Snell's Law and how it applies to layers in the earth. It addresses reflected, refracted, critically refracted, and head waves. And ends with a quiz about which path is the fastest to seismic stations 30-100 meters away. Seismic waves travel at different speeds through different materials. In this 2-layer model two wave fronts leave an impact at the same time but the lower layer is faster.
CLOSED CAPTIONING: A .srt file is included with the downloiad. Use appropriate media player to utilize captioning.
Snells Law describes how seismic ray paths bend as they travel from one material into another.
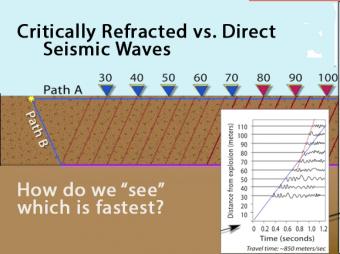
Animation shows the race between the direct seismic wave vs. the deeper, longer-path critically refracted seismic wave. Graph records the arrival times.

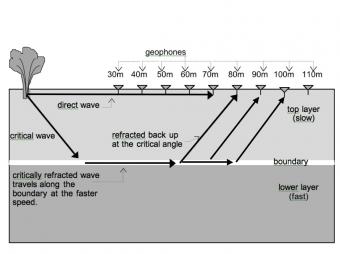
Like other waves, seismic waves obey the laws of physics. In this activity Physics students have the opportunity to apply their understanding of the basic concepts of waves (e.g. reflection, refraction and transmission of energy) as they examine seismic data to determine how far it is from the surface to the bedrock.
We encourage the reuse and dissemination of the material on this site as long as attribution is retained. To this end the material on this site, unless otherwise noted, is offered under Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license