8min 45s Novice Spanish
This animation explores three major mechanisms for earthquakes in South America due to the interaction of the Nazca and South American plates.
CLOSED CAPTIONING: A .srt file is included with the downloiad. Use appropriate media player to utilize captioning.
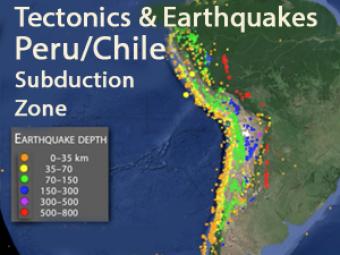
Western South America is a region of high earthquake hazard because of:
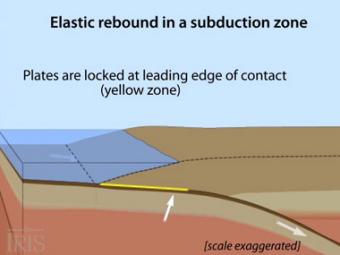
Oblique view of a highly generalized animation of a subduction zone where an oceanic plate is subducting beneath a continental plate. (See sketch below for parts.) This scenario can happen repeatedly on a 100-500 year cycle. The process which produces a mega-thrust earthquake would generate a tsunami, not depicted here.
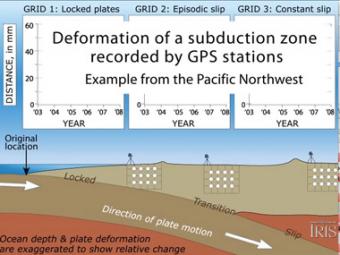
Subduction zones show that there are 3 distinct areas of movement in the overlying plate:
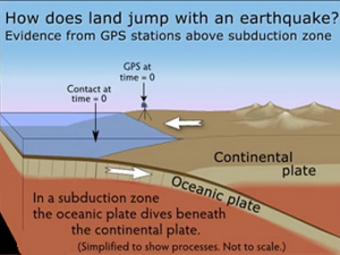
GPS can record the movement of the leading edge of the overlying continental plate in a subduction zone. The plates are locked and the overlying plate is forced back. When friction is overcome and strain is released, the GPS receiver will snap back toward its original position.
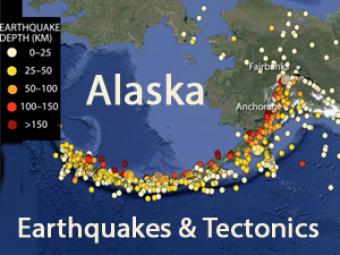
Alaskan tectonics are dominated by the Pacific-North American plates. The megathrust boundary between the plates results in both the 4,000-km-long Aleutian Trench and in the arc of active volcanoes that lie subparallel to the trench.
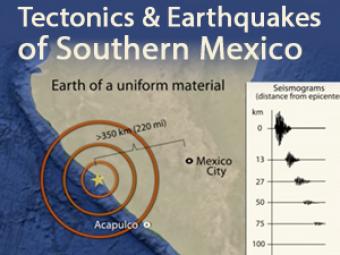
In 1985, a Great, magnitude 8.1 subduction zone earthquake occurred beneath the coast of Michoacan, Mexico causing over 9,000 fatalities over 350 km away. What caused it and how has Mexico instituted their Earthquake Early Warning system? This animation describes the mechanics.
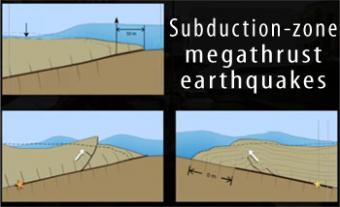
Subduction-zone megathrust earthquakes, the most powerful earthquakes in the world, can produce tsunamis through a variety of structures that are missed by simple models including: fault boundary rupture, deformation of overlying plate, splay faults and landslides. From a hazards viewpoint, it is critical to remember that tsunamis are multiple waves that often arrive on shore for many hours after the initial wave.
We encourage the reuse and dissemination of the material on this site as long as attribution is retained. To this end the material on this site, unless otherwise noted, is offered under Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license