Novice English English English
Tectonic plates are constantly moving, and GPS instruments anchored to the ground help measure these motions over time. Scientists use GPS data to identify plate boundaries, deformation zones, and earthquake hazards, with regions showing rapid changes in movement being at higher seismic risk.
This triad of activities helps learners explore and interpret authentic GPS data to understand plate motion in the western U.S. and Alaska:
In this 5-Minute Activity, learners use hand movements to demonstrate different tectonic plate boundary types and understand how ground motion varies in speed and direction. After learning about vectors, they apply this knowledge to real-world plate motion scenarios, interpreting tectonic movements as measured by GPS instruments.
In this 20-minute Activity, learners work in pairs to create vectors using a compass rose to understand how vectors represent direction and speed. They then explore GPS vector ground motion maps or the GPS Velocity Viewer to observe areas where ground motion is consistent and areas where speed and direction vary, helping them analyze tectonic plate boundary movements.
In this 50-Minute Activity, learners explore GPS data to analyze how the western U.S. is moving, identifying regions where tectonic plates interact and deformation builds up, leading to earthquakes. Through data jigsawing and role-playing geoscience careers, they investigate the relationships between earthquakes, volcanoes, plate movement, topography, and hazards, concluding with an introduction to the ShakeAlert Earthquake Early Warning System.
This activity sequence not only builds data interpretation skills but also introduces careers in geodesy, seismology, and volcanology. Understanding plate motion and ground deformation is crucial, as over 143 million people in the U.S. are at risk from earthquakes. Tools like ShakeAlert, which integrates GPS data, enhance hazard preparedness by detecting and quickly warning about earthquakes.
Learners will be able to:
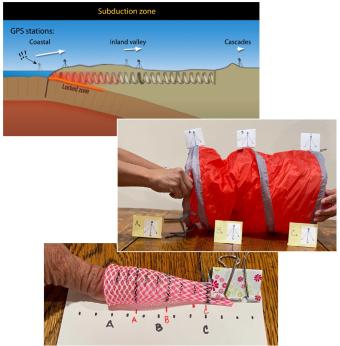
This set of hands-on activities helps students investigate ground deformation and earthquake hazards in the Pacific Northwest using physical models, real-world data, and map analysis. A brief demonstration with a compression spring illustrates how the subduction of the Juan de Fuca plate beneath the North American plate causes varying motion across the region. In longer activities, students measure compression, analyze GPS vector maps, and identify seismic hazard zones. By interpreting real-world data, students develop a deeper understanding of tectonic forces and connect these concepts to earthquake preparedness strategies.
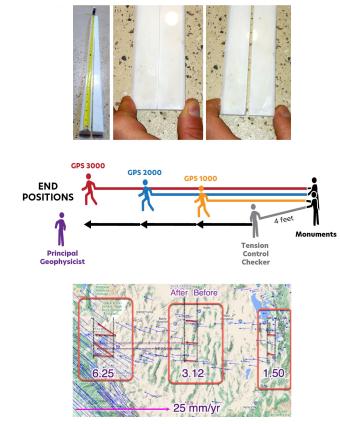
Ground deformation occurs both at plate boundaries and within plates, such as the Basin and Range Province in Nevada, Utah, and California, where extension and rifting can be measured using GPS data. This triad of activities helps learners explore deformation through hands-on modeling with marble tongs, kinesthetic demonstrations of extensional motion, and quantitative analysis of GPS vectors and earthquake hazard maps. Understanding these processes is crucial, as over 143 million people in the U.S. face earthquake risks, and tools like ShakeAlert use GPS data to provide early warnings that can help reduce damage and save lives.

In this activity, learners explore ground deformation at and near plate boundaries using hand and body motions, data from GPS and maps. In the 5-minute activity, learners explore the concept of vectors by kinesthetically enacting ground movement using their body and hand movements. In the 20-minute activity, learners model GPS ground motion in different regions and connect deformation to earthquake hazards. In the 45-minute activity learners distinguish between different boundary types by measuring the vectors within tectonic plates and identify regions with higher earthquake hazards, comparing their findings to earthquake shaking potential maps.
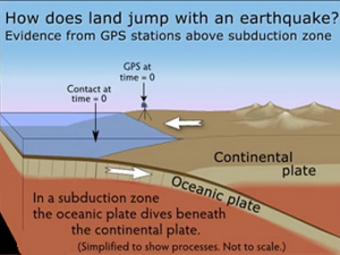
GPS can record the movement of the leading edge of the overlying continental plate in a subduction zone. The plates are locked and the overlying plate is forced back. When friction is overcome and strain is released, the GPS receiver will snap back toward its original position.
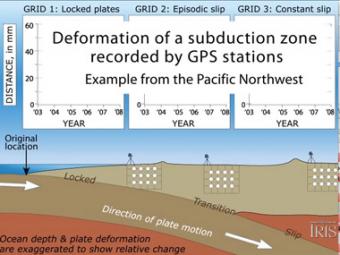
Subduction zones show that there are 3 distinct areas of movement in the overlying plate:
We encourage the reuse and dissemination of the material on this site as long as attribution is retained. To this end the material on this site, unless otherwise noted, is offered under Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license